Facial pigmentation can be broadly categorized into two types: passive and post-inflammatory. Passive pigmentation arises from internal activation, with causes often linked to hormonal fluctuations, pregnancy, and certain medications that trigger an increased production of melanin—the pigment responsible for skin color. On the other hand, post-inflammatory pigmentation results from external factors or trauma to the skin. Unlike passive pigmentation, post-inflammatory pigmentation is more superficial and can be linked directly to specific incidents or external forces. This characteristic makes it easier to identify the cause and subsequently treat it permanently, offering individuals affected by this type of pigmentation a clearer path to achieving balanced and radiant skin
Pigmentation
Understanding the intricacies of individual skin pigmentation.
Several Common Forms Of Pigmentation
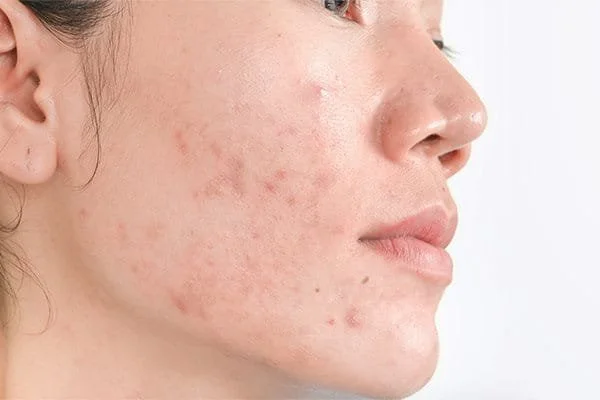
Post-Inflammatory Pigmentation
Post-Inflammatory Pigmentation results in darkened skin areas due to trauma, injury, or inflammation, often triggered by wounds, acne, or skin conditions. These dark spots occur as a response to increased melanin production. Fortunately, this type of pigmentation is usually more superficial, making it easier to treat. Solutions include topical treatments like retinoids, vitamin C, or niacinamide, along with procedures such as chemical peels or laser therapy. Consistent skincare routines and proper sun protection are essential in reducing and preventing post-inflammatory pigmentation, helping restore a more even skin tone.
Melasma
Melasma is characterized by the appearance of dark facial patches, is commonly triggered by hormonal changes, especially during pregnancy or due to oral contraceptive use. Sun exposure further intensifies these pigmentation irregularities. To effectively address melasma, individuals should prioritize daily sun protection using high SPF sunscreen. Topical treatments, such as hydroquinone and vitamin C, can aid in lightening dark patches. In addition to topical solutions, procedures like chemical peels and laser therapy, guided by a qualified medical esthetician, may be considered for more resistant cases.
Sun Damage
Sun-damaged skin stems from prolonged exposure to UV radiation, causing issues like sunspots and fine lines. UV rays prompt melanin production, leading to uneven pigmentation and an increased risk of skin aging and cancers. To counteract sun damage, incorporate daily sunscreen use and protective measures. Skincare with antioxidants and retinoids, along with chemical peels, can help address existing damage and promote a healthier complexion. Consistent sun protection is key in preventing further harm and maintaining youthful skin.
Freckles
Freckles are small, flat spots on the skin caused by increased melanin production in response to sunlight. Common on sun-exposed areas, such as the face, arms, and shoulders, freckles are more noticeable in individuals with fair skin. While generally harmless, they signify the skin's reaction to sun exposure. Preventive measures include regular sunscreen use. Treatments like laser therapy, chemical peels and skincare that helps to inhibit pigment can lighten freckles for those seeking it. I believe embracing these unique features adds to the diversity and individuality of each person's skin.